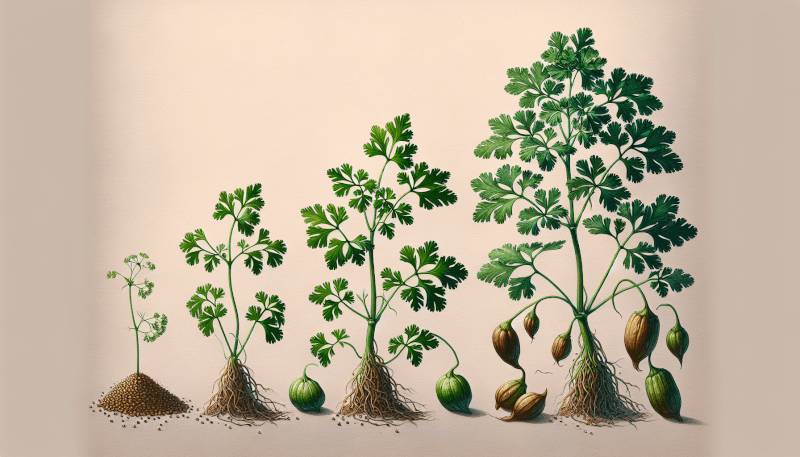Coriander, a versatile and aromatic herb used in cuisines all over the world, not only adds a burst of flavor to your dishes but also provides a delightful touch to your garden. If you’ve ever wondered how to cultivate these tiny seeds and enhance your culinary endeavors, look no further! In this article, we will guide you through the art of harvesting coriander seeds, uncovering the secrets to a bountiful harvest that will elevate your cooking to new heights. Get ready to embark on a journey of discovery as we unveil the wonders of reaping the rewards of coriander cultivation.
When to Harvest Coriander Seeds
Understanding the Growth Cycle
Harvesting coriander seeds requires careful observation of the plant’s growth cycle. Coriander, also known as cilantro or Chinese parsley, is an annual herb that goes through distinct stages of growth. It starts as a small seedling, then develops into a leafy plant with fragrant leaves. Eventually, it flowers and produces seeds. Understanding these stages will help you determine the optimal time for harvesting coriander seeds.
Monitoring the Plant for Seed Development
To know when it’s time to harvest coriander seeds, you need to closely monitor the plant for seed development. After the coriander plant flowers, it takes some time for the seeds to fully develop. You will notice small green seed pods forming, which will eventually turn brown as they mature. Regularly check the plant for these changes and keep an eye on the progression of seed development.
Determining the Optimal Time for Harvest
The optimal time for harvesting coriander seeds is when the seed pods have turned brown and are slightly dry. At this stage, the seeds are fully mature and have the most flavor. However, you should harvest them before they start to shatter and release the seeds on their own. Timing is crucial, as harvesting too early will result in immature seeds with less flavor, while waiting too long may lead to loss of seeds.
Preparing for Harvest
Gathering the Necessary Tools and Equipment
Before you begin harvesting coriander seeds, gather the necessary tools and equipment. These include a pair of clean pruning shears or scissors, a small knife, a tray or basket for collecting seeds, and gloves to protect your hands. Having these supplies ready will make the harvesting process more efficient and ensure that you can handle the seeds properly.
Choosing the Right Harvesting Method
There are several methods you can choose from when harvesting coriander seeds. The method you use depends on personal preference and the size of your coriander plants. The three commonly used methods are handpicking individual seeds, cutting and collecting seed heads, and bagging seeds for indirect collection. Each method has its own advantages and considerations, so choose the one that suits your needs best.
Preparing the Harvesting Area
Before you start harvesting coriander seeds, it’s important to prepare the harvesting area. Clear any debris or weeds around the coriander plants to provide easier access. You may also want to lay a clean cloth or tarp underneath the plants to catch any seeds that may fall during the process. By preparing the harvesting area in advance, you can ensure a clean and organized harvest.
Harvesting Techniques
Method 1: Handpicking Individual Seeds
Handpicking individual seeds is a suitable method if you have a small coriander plant or only a few plants to harvest from. This method requires patience and attention to detail. Simply hold a seed head between your thumb and forefinger and gently rub the seed pods to release the seeds into your collection tray or basket. Continue this process until you have harvested all the mature seeds from the plant.
Method 2: Cutting and Collecting Seed Heads
If you have a larger coriander plant with multiple seed heads, cutting and collecting seed heads may be a more efficient method. Use clean pruning shears or scissors to cut the seed heads from the plant. Place the cut seed heads in a tray or basket, being careful not to jostle or drop them to avoid premature seed release. Once you have collected all the seed heads, proceed to the next steps for drying and cleaning.
Method 3: Bagging Seeds for Indirect Collection
Bagging seeds for indirect collection is a method that allows you to collect seeds without directly handling the seed heads. This method is especially useful if you want to collect seeds from multiple plants at once or have limited time for harvesting. Simply place a small paper or mesh bag over the seed heads and secure it with a twist tie or rubber band. As the seed heads mature and naturally release their seeds, they will collect in the bag for easy collection later.
Post-Harvest Practices
Drying Coriander Seeds
After harvesting coriander seeds, it is important to dry them properly to prevent mold or rot. Spread the seeds in a single layer on a clean, dry tray or cloth. Place them in a warm and well-ventilated area out of direct sunlight. Stir the seeds occasionally to ensure even drying. It can take anywhere from one to two weeks for the seeds to fully dry, depending on the humidity levels in your area.
Cleaning and Removing Debris
Once the coriander seeds are completely dry, it’s time to clean and remove any debris. Gently rub the dried seeds between your palms or use a clean cloth to remove any remaining chaff. You can also use a sieve or fine mesh screen to separate the seeds from the debris. Be thorough and take your time to ensure that you have clean, pure coriander seeds ready for storage.
Storing Seeds Properly
To keep your harvested coriander seeds fresh and flavorful for an extended period, proper storage is essential. Transfer the cleaned seeds into airtight containers, such as glass jars or resealable bags. Store them in a cool, dry, and dark place to maintain their quality. If stored correctly, coriander seeds can last up to one year without significant loss of flavor or potency.
Extending Harvest Season
Successive Planting for Continuous Seed Production
To extend the harvest season of coriander seeds, consider successive planting. Rather than sowing all the coriander seeds at once, stagger your plantings every few weeks. This will ensure a continuous supply of fresh coriander plants and a steady stream of seed production throughout the growing season. By carefully planning your plantings, you can maximize your coriander seed harvest.
Promoting Flowering and Seed Formation
To encourage flowering and seed formation in coriander plants, provide them with optimal growing conditions. Coriander prefers full sun but can tolerate some shade, especially in hotter regions. Regularly water the plants, keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Applying a balanced fertilizer during the vegetative stage can also promote healthy growth and increase the chances of successful seed formation.
Minimizing Stress Factors
Stress factors can affect coriander plants’ ability to produce seeds. Avoid subjecting the plants to extreme temperatures, as excessive heat or cold can hinder seed development. Additionally, ensure that the plants are not overcrowded, as this can lead to competition for nutrients and space, reducing seed production. By minimizing stress factors, you can help your coriander plants thrive and optimize seed harvest.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Seed Predators and Infestation
Coriander seeds are vulnerable to seed predators and infestation. Common pests that can attack coriander seeds include weevils, aphids, and mites. To prevent these pests from causing damage, regularly inspect the coriander plants for signs of infestation. If necessary, use appropriate organic pest control methods to deter or eliminate the pests. Proper storage of harvested seeds can also prevent infestation during the post-harvest phase.
Fungal and Bacterial Diseases
Fungal and bacterial diseases can also pose a threat to coriander seed production. Damping-off, powdery mildew, and bacterial leaf spots are common diseases that affect coriander plants. To prevent these diseases, ensure proper air circulation and avoid overwatering, as these conditions promote fungal growth. If disease symptoms appear, treat the plants with organic fungicides or bactericides to prevent the spread and protect the seed production.
Environmental Factors Affecting Seed Production
Coriander seed production can be influenced by various environmental factors. Extreme temperatures, such as heatwaves or cold snaps, can impact flowering and seed formation. Excessive rainfall or waterlogging can also negatively affect seed development. By understanding the specific environmental requirements of coriander and providing suitable conditions, you can mitigate these factors’ impact on seed production.
Enhancing Seed Quality and Yield
Selecting High-Quality Seed Varieties
To enhance the quality and yield of coriander seeds, choose high-quality seed varieties. Look for reputable seed suppliers and opt for certified organic or heirloom varieties. These varieties are often more resistant to diseases and pests, ensuring better seed production. Conducting thorough research and selecting suitable seed varieties will set the foundation for successful coriander seed harvesting.
Proper Planting and Spacing
Proper planting and spacing of coriander plants are essential for optimum seed production. Sow the seeds at the appropriate depth, usually around ¼ inch deep, and provide enough space between plants for air circulation. Overcrowding can lead to competition for resources and reduce seed yields. Follow the recommended planting guidelines for your specific coriander variety to ensure successful seed production.
Providing Adequate Nutrition and Water
Coriander plants require adequate nutrition and water for healthy growth and seed production. Incorporate organic matter into the soil before planting to ensure proper nutrient availability. Additionally, provide regular watering, especially during dry periods, to keep the soil consistently moist. Adequate nutrition and water will support the plants’ overall health and optimize the seed quality and yield.
Alternative Uses for Coriander Seeds
Culinary Applications and Spice Blends
Coriander seeds are a versatile spice used in various culinary applications and spice blends. They have a warm, citrusy flavor that pairs well with savory dishes, particularly in Indian, Mexican, and Middle Eastern cuisines. Ground coriander seeds can be used as a seasoning for meats, vegetables, and sauces, as well as in baked goods and desserts. Experiment with different recipes and spice blends to make the most of your coriander seeds.
Herbal Remedies and Medicinal Uses
In addition to its culinary uses, coriander seeds have been traditionally used for their medicinal properties. They are known to aid digestion, relieve stomach discomfort, and promote overall digestive health. Coriander seeds can be brewed into a herbal tea or incorporated into herbal remedies for various ailments. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before using coriander seeds for medicinal purposes.
Non-Food Applications
Coriander seeds can also have non-food applications. They have a pleasant aroma that makes them suitable for use in potpourri, sachets, and scented candles. The essential oil extracted from coriander seeds is used in perfumes, soaps, and beauty products. Consider exploring the non-food uses of coriander seeds to fully utilize their aromatic and sensory qualities.
Tips for Sustainable Harvesting
Practicing Organic Methods
When harvesting coriander seeds, it is important to practice organic methods to minimize the impact on the environment. Avoid using synthetic pesticides or fertilizers that can harm beneficial insects and soil health. Instead, opt for organic pest control measures, such as companion planting and natural insect repellents. By practicing organic methods, you contribute to sustainable agricultural practices and promote a healthier ecosystem.
Implementing Crop Rotation
To maintain soil fertility and reduce the risk of diseases and pests, implement crop rotation when growing coriander. Avoid planting coriander in the same area year after year to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases specific to this plant. Rotate coriander with other unrelated crops to break the pest and disease cycle. This practice helps maintain the health of your coriander plants and ensures a sustainable harvest.
Promoting Pollinator-Friendly Practices
Coriander plants rely on pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, for successful seed production. To attract and support pollinators, create a pollinator-friendly environment in your garden. Plant a variety of flowering plants to provide nectar and pollen sources throughout the season. Avoid using pesticides that can harm pollinators and provide shelter, such as bee houses or butterfly-friendly plants. Promoting pollinator-friendly practices contributes to a healthy and abundant coriander seed harvest.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Harvesting coriander seeds requires understanding the growth cycle and monitoring the plant for seed development. Gathering the necessary tools, choosing the right harvesting method, and preparing the harvesting area are crucial steps to ensure a successful harvest. Different techniques, such as handpicking individual seeds, cutting and collecting seed heads, or bagging seeds for indirect collection, can be used to harvest coriander seeds. Post-harvest practices, including drying, cleaning, and proper storage, are essential for preserving seed quality. To extend the harvest season, successive planting, promoting flowering, and minimizing stress factors can be implemented. Common issues such as seed predators, diseases, and environmental factors affecting seed production can be addressed through proper pest control and disease management. Enhancing seed quality and yield can be achieved through careful selection of seed varieties, proper planting and spacing, and providing adequate nutrition and water. Coriander seeds have various alternative uses in culinary, medicinal, and non-food applications. Practicing sustainable harvesting methods, such as organic practices, crop rotation, and promoting pollinator-friendly practices, is vital for preserving the environment and ensuring a sustainable harvest.
Final Thoughts on Harvesting Coriander Seeds
Harvesting coriander seeds can be a rewarding experience for any home gardener or herb enthusiast. By carefully following the growth cycle, monitoring the plant’s development, and using the appropriate harvesting techniques, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of flavorful coriander seeds. With proper post-harvest practices and storage, you can savor the taste and aroma of coriander throughout the year. Remember to embrace the versatility of coriander seeds, exploring their culinary, medicinal, and non-food applications. Implementing sustainable harvesting practices is not only beneficial for your own harvest but also contributes to a healthier environment and supports the pollinators that play a crucial role in coriander seed production. So, put on your gardening gloves, gather your tools, and get ready to enjoy the abundant harvest of coriander seeds!