👋 Click the mic button to talk to Alfred, the Todd's Seeds Gardening/Sprouting Expert – Feel free to ask him anything!
Ask Virtual Todd Anything - Click the Mic
Imagine walking through a vibrant field, seemingly painted in shades of red, as a soft breeze brushes against your skin. In this captivating landscape, one flower stands out amongst the rest – the crimson clover. With its brilliant crimson petals and clover-shaped leaves, this stunning plant not only adds beauty to the environment but also offers a host of benefits. From enriching the soil with nitrogen to providing a source of nourishment to honeybees, the crimson clover is a true gem in nature’s tapestry. Discover the wonders of this remarkable flower and the role it plays in enhancing our surroundings.
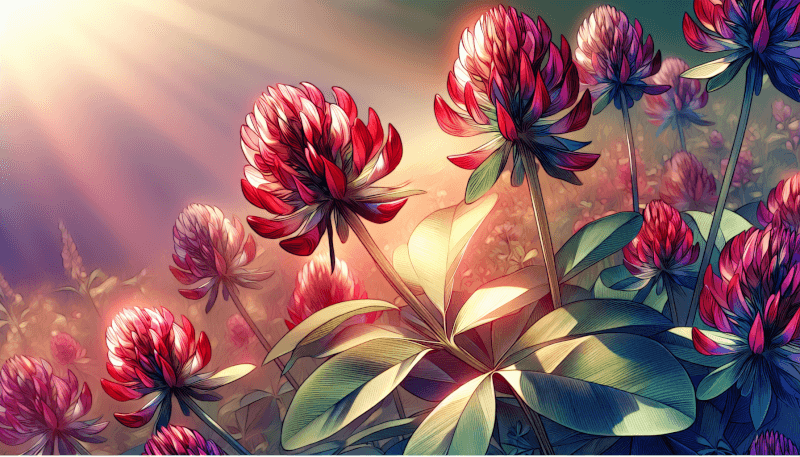
What is Crimson Clover?
Crimson clover, scientifically known as Trifolium incarnatum, is a species of clover that belongs to the legume family. It is a popular cover crop and forage crop due to its ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, improve soil health, and provide valuable forage for livestock. Crimson clover gets its name from its vibrant crimson flowers, which add a splash of color to fields and gardens. Let’s dive into the appearance, origin, and uses of this versatile plant.
Appearance
Crimson clover is an annual herbaceous plant that typically reaches a height of around 1 to 2 feet when fully grown. Its leaves consist of three leaflets, giving it the characteristic trifoliate appearance common to clovers. The leaflets are oval-shaped and have a smooth texture. However, what truly sets crimson clover apart is its striking flowers. These vibrant red flowers grow in dense, cone-shaped clusters and attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
Origin
Crimson clover is native to the Mediterranean region of Europe but has now naturalized throughout many parts of the world. It was introduced to the United States in the early 1800s and has since become widely cultivated. The plant thrives in moderate climates with mild winters and moderate rainfall. Crimson clover is known for its adaptability and can grow in a variety of soil types.
Uses
With its myriad of benefits, crimson clover serves multiple purposes in both agriculture and horticulture. Its primary uses include soil improvement, nitrogen fixation, weed suppression, and providing habitat for beneficial wildlife. Additionally, crimson clover is employed as a cover crop, forage crop, and green manure. Let’s explore each of these uses in more detail.
Types of Crimson Clover
Crimson clover is available in several different varieties, each with its own unique characteristics. The most common types of crimson clover include Medium Red Clover, Dwarf Red Clover, and Arlington Crimson Clover.
Medium Red Clover
Medium Red Clover, also known as Early Blood Red Clover, is a popular choice for cover cropping. It typically grows taller than other varieties, reaching heights of 12 to 24 inches. This type of crimson clover provides excellent weed suppression, helps control erosion, and attracts pollinators with its vibrant flowers. It is often sown as part of a crop rotation system to enhance soil fertility and organic matter.
Dwarf Red Clover
Dwarf Red Clover, as the name suggests, is a compact variety that grows to a height of around 6 to 12 inches. It is well-suited for low-growing cover crops and makes an excellent companion plant in vegetable gardens. Dwarf Red Clover fixes nitrogen in the soil efficiently, enriching it with this essential nutrient. Its lower height also makes it less competitive with crops and easier to manage.
Arlington Crimson Clover
Arlington Crimson Clover is a newer variety that has gained popularity for its adaptability and high seed production. It has a bushy growth habit, reaching heights of 12 to 18 inches, and produces abundant crimson flowers. Arlington Crimson Clover is often used as a winter annual cover crop due to its ability to tolerate colder temperatures. It helps suppress weeds, improves soil health, and attracts pollinators to the garden or field.
Cultivation of Crimson Clover
To ensure successful cultivation of crimson clover, it is essential to understand its specific soil requirements, the planting process, and the necessary maintenance practices.
Soil Requirements
Crimson clover thrives in well-drained soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. It prefers loamy soils but can tolerate a wide range of soil types, including sandy and clay soils. However, it is crucial to avoid heavy, poorly drained soils, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot and other diseases. Prior to planting, it is recommended to conduct a soil test and amend the soil with organic matter or lime if necessary.
Planting
Crimson clover is typically sown in late summer or early fall, depending on the region’s climate and desired use of the plant. The seeds should be sown at a rate of 15 to 20 pounds per acre for cover cropping and up to 30 pounds per acre for forage production. Before sowing, the soil should be prepared by removing any existing weeds and debris. Broadcasting the seeds evenly over the prepared ground and lightly raking them into the soil will promote optimal germination.
Maintenance
Once established, crimson clover requires minimal maintenance. Regular monitoring for weeds is important, especially during the early stages of growth. Additional weed control measures, such as hand weeding or strategic mowing, may be necessary in more weed-prone areas. Adequate moisture is essential, particularly during dry spells, to promote healthy growth. In some cases, irrigation may be required to supplement rainfall. However, it is important to avoid overwatering, as excessive moisture can lead to disease.
Benefits of Crimson Clover
Crimson clover offers a range of benefits that make it a valuable addition to any agricultural or horticultural system. Let’s explore the key advantages provided by this remarkable plant.
Nitrogen Fixation
One of the primary benefits of crimson clover is its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a plant-available form. Like other legumes, it forms a symbiotic relationship with specific bacteria called rhizobia, which reside in nodules on the plant’s roots. These bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is then utilized by the plant. This process significantly improves soil fertility and reduces the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers.
Soil Improvement
In addition to nitrogen fixation, crimson clover contributes to soil improvement through its extensive root system. The deep taproot of the plant helps break up compacted soil, enhancing both water infiltration and aeration. As the plant decomposes after termination, it adds organic matter to the soil, promoting soil structure and moisture retention. This organic matter also provides a food source for beneficial microorganisms, further enriching the soil ecosystem.
Wildlife Habitat
Crimson clover’s vibrant flowers and nutritious forage make it a valuable habitat for pollinators, such as bees and butterflies. These insects play a crucial role in pollinating crops and supporting overall ecosystem health. By planting crimson clover, you can create inviting habitats that support these essential pollinators and contribute to biodiversity. Furthermore, the plant’s dense growth provides cover and nesting opportunities for a variety of wildlife species.
Uses of Crimson Clover
The versatility of crimson clover extends beyond its soil-improving qualities. This remarkable plant finds various applications in agriculture, gardening, and land management. Let’s explore its primary uses in more detail.
Cover Crop
Crimson clover is widely used as a cover crop due to its numerous benefits. As a cover crop, it protects the soil from erosion, reduces weed growth, and increases soil fertility. Planting crimson clover as a cover crop during fallow periods or in between cash crops helps maintain soil health and prevents nutrient leaching. Its extensive root system also aids in preventing soil compaction.
Forage Crop
Crimson clover is an excellent source of high-quality forage, making it a valuable crop for livestock production. Both the foliage and flowers of crimson clover are highly palatable to grazing animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats. It provides essential nutrients, including protein and minerals, and can be grazed or harvested as hay or silage. Incorporating crimson clover in livestock grazing systems improves animal diet and overall forage production.
Green Manure
The use of crimson clover as a green manure has gained popularity among organic farmers and gardeners. Green manure refers to the practice of incorporating living or fresh plant material into the soil to improve its fertility and structure. By growing crimson clover as a green manure crop, you can add organic matter, increase nitrogen levels, improve soil health, and suppress weeds naturally. It serves as an effective way to enrich the soil without relying on synthetic fertilizers.
Crimson Cover and Beekeeping
Crimson clover plays a vital role in supporting bee populations and promoting honey production. Its vibrant red flowers attract bees and other pollinators, providing them with a valuable source of nectar and pollen. The continuous blooming period of crimson clover ensures a consistent food source for bees, contributing to their overall health and vitality. Beekeepers often strategically plant crimson clover near their hives, creating an abundant foraging ground that enhances honey production.
Attracting Bees
The bright red flowers of crimson clover act as a beacon, attracting bees from far and wide. Bees are drawn to the rich nectar and pollen that the flowers provide, making them frequent visitors to crimson clover fields and gardens. By planting crimson clover, you can create an inviting habitat that supports bee populations and helps sustain their vital role as pollinators.
Honey Production
The presence of crimson clover in beekeeping operations can significantly enhance honey production. Bees collect nectar from the crimson clover flowers, which they use to produce honey. The vibrant red color of the flowers adds a unique flavor and aroma profile to the honey, providing beekeepers with a distinct product loved by consumers. Additionally, the high-quality forage provided by crimson clover ensures that bees have access to the necessary resources for optimal honey production.
Crimson Clover and Weed Suppression
Weed control is a constant challenge in agricultural and horticultural practices. Crimson clover can play a beneficial role in suppressing weeds through its allelopathic effects and by covering bare soil.
Allelopathic Effects
Crimson clover exhibits allelopathic properties, which means it releases natural chemicals that inhibit the growth of certain weed species. These allelochemicals can impede weed seed germination and reduce weed competition, giving crimson clover a competitive advantage. While suppressing weeds, crimson clover thrives, allowing it to effectively cover the soil and provide its numerous benefits.
Covering Bare Soil
Bare soil is highly susceptible to weed growth, erosion, and nutrient loss. Crimson clover acts as a living mulch, covering the soil and preventing weed seeds from germinating. Its dense growth prevents sunlight from reaching the soil surface, reducing weed establishment. By covering bare soil, crimson clover helps maintain soil moisture, reduce erosion, and create a favorable environment for beneficial soil organisms.
Crimson Clover as a Companion Plant
Crimson clover’s versatility is further demonstrated by its effectiveness as a companion plant. It can be strategically planted alongside vegetables and fruit trees to provide various benefits.
Companion to Vegetables
When planted as a companion to vegetables, crimson clover acts as a living mulch and weed suppressor. Its dense growth and allelopathic properties help smother weeds, minimizing competition with the main vegetable crops. The crimson clover also helps regulate soil temperature by providing shade and acts as a natural nutrient accumulator, cycling nutrients back into the soil as it decomposes. In return, the vegetables provide support for the upward growth of the crimson clover, creating a mutually beneficial relationship.
Companion to Fruit Trees
Crimson clover can also serve as a beneficial companion plant for fruit trees. When planted around the base of fruit trees, it acts as a natural ground cover, reducing weed growth, conserving soil moisture, and preventing erosion. The nitrogen-fixing abilities of crimson clover improve the overall fertility of the soil, providing essential nutrients to the fruit trees. Furthermore, the presence of crimson clover attracts pollinators, ensuring proper fruit set and maximizing yield.
Shortcomings and Limitations
While crimson clover possesses numerous benefits, it is essential to consider its potential shortcomings and limitations to ensure successful integration into agricultural and horticultural systems.
Cold Sensitivity
Crimson clover is sensitive to cold temperatures and may not survive severe frosts or extended freezing periods. Therefore, it is primarily cultivated in regions with mild winters or used as a winter annual cover crop in areas where winters are too harsh for it to overwinter successfully.
Competitiveness with Crops
Crimson clover’s vigorous growth can sometimes compete with cash crops, particularly if not properly managed. It is crucial to strategically time termination or incorporation of the crimson clover to avoid competition for resources such as water, light, and nutrients. Additionally, careful consideration should be given to the choice of crimson clover variety and its specific growth habit to minimize any negative impacts on the associated crops.
Potential Allergenicity
While crimson clover is not classified as highly allergenic, it can still induce allergic reactions in some individuals, particularly those with existing sensitivities to plant pollen. It is important to be aware of any potential allergenicity and take necessary precautions when handling or being in close proximity to crimson clover, especially during its flowering period.
Conclusion
Crimson clover, with its vibrant crimson flowers and numerous benefits, is a valuable addition to any agricultural or horticultural system. From its nitrogen-fixing capabilities to its soil improvement properties, this versatile plant serves as an outstanding cover crop, forage crop, and green manure. Its role in supporting bee populations, suppressing weeds, and acting as a companion plant further highlights its versatility and significance. However, it is crucial to understand the specific requirements and limitations of crimson clover to maximize its potential benefits. By harnessing the power of crimson clover, you can enhance soil health, promote biodiversity, and achieve sustainable and productive farming and gardening practices.


