👋 Click the mic button to talk to Alfred, the Todd's Seeds Gardening/Sprouting Expert – Feel free to ask him anything!
Ask Virtual Todd Anything - Click the Mic
Growing your own plants from seeds can be a fulfilling and rewarding experience. It allows you to bring a touch of nature and greenery into your home, even if you don’t have a garden or outdoor space. In this article, we will explore the art of sprouting seeds indoors, offering you practical tips and techniques to get started on your own indoor garden. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, this guide will help you unlock the secrets to successful seed germination and nurture healthy and vibrant plants right in the comfort of your own home. So, grab your gardening gloves and let’s embark on this exciting journey of sprouting seeds indoors together!
Choosing the Right Seeds
Consider the Purpose of Sprouting
When choosing seeds for sprouting indoors, it’s important to consider what you want to achieve with your sprouts. Are you looking to grow vegetables, herbs, or flowers? Different seeds have varying requirements and grow at different rates, so it’s important to select seeds that align with your goals.
Research Different Seed Varieties
Do some research to find out which seeds are best suited for indoor sprouting. Consider factors such as their nutritional value, growth habits, and compatibility with indoor growing conditions. Some popular options for indoor sprouting include tomatoes, lettuce, basil, and sunflowers.
Check for Seed Viability
Before purchasing or using seeds for sprouting, it’s important to check their viability. Seeds that are old or expired may not germinate as well or at all. Perform a simple viability test by placing a few seeds on a damp paper towel and sealing them in a plastic bag. Check on them after a few days to see if they have sprouted. This will help you ensure that you are working with healthy and viable seeds.
Consider the Space Available
Consider the space you have available for your indoor sprouting project. If you have limited space, you might want to focus on smaller plants or choose seeds that can be easily contained or trellised. On the other hand, if you have ample space, you can experiment with a variety of plants and grow a larger quantity of sprouts.
Gathering the Necessary Supplies
Container Selection
Choose containers that are suitable for sprouting seeds indoors. Look for containers that provide drainage to prevent waterlogging and promote healthy root development. You can use trays, pots, or even recycled materials like egg cartons or yogurt containers.
Seed Starting Mix
To provide the optimal growing conditions for your seeds, you’ll need a quality seed starting mix. This mix should be lightweight, well-draining, and nutrient-rich. Avoid using garden soil, as it can be too heavy and may contain pathogens or weed seeds. Seed starting mixes can be purchased from gardening stores or you can make your own by combining peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite.
Watering Supplies
Having the right watering supplies is crucial for successful indoor sprouting. Make sure you have a spray bottle for gentle misting, a watering can with a fine spout, and a tray or saucer to catch excess water. It’s important to water your sprouts regularly and evenly to maintain proper moisture levels.
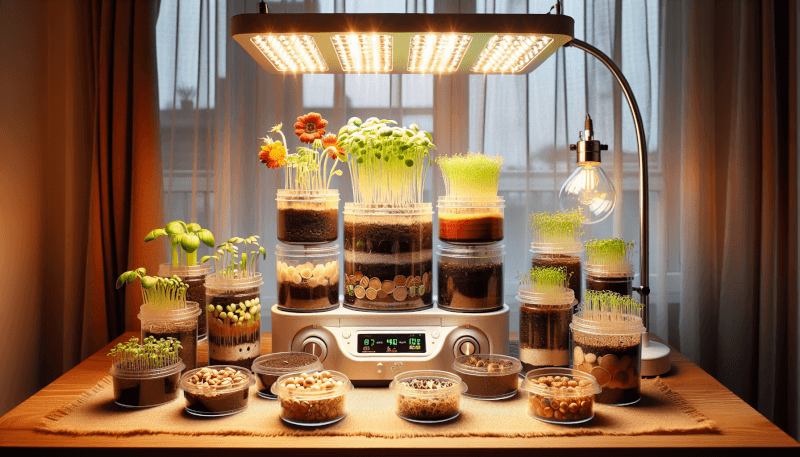
Light Source
Since indoor sprouting lacks natural sunlight, you’ll need to provide an artificial light source. LED grow lights are a popular choice as they are energy-efficient and emit the specific wavelengths of light that plants need for photosynthesis. Position the lights about 6-12 inches above your sprouts, adjusting the height as they grow. A timer can be used to ensure consistent light exposure.

Preparing the Seeds for Sprouting
Seed Soaking
Some seeds benefit from pre-soaking before planting to promote germination. Soaking seeds overnight or for a few hours can help soften the seed coat and speed up germination. However, not all seeds require soaking, so be sure to check the specific requirements for the seeds you’re using.
Pre-germination Techniques
Some seeds may require additional pre-germination techniques to improve germination rates. This can include scarification, which involves scratching or nicking the seed coat, or stratification, which involves exposing the seeds to a period of cold temperatures to simulate winter conditions. Follow the instructions provided for each seed variety to ensure successful germination.
Setting Up the Indoor Growing Environment
Choosing a Suitable Location
Find a suitable location in your home for your indoor sprouting project. Ideally, this should be a place that receives sufficient light and is away from drafts or temperature extremes. Consider using a dedicated shelving unit, windowsill, or countertop to create your growing space.
Maintaining Optimal Temperature
Most seeds require specific temperature ranges for germination. Ensure that the room temperature is within the optimal range for the seeds you’re sprouting. You can use a thermometer to monitor the temperature and make necessary adjustments, such as using a heating mat or adjusting the thermostat.
Providing Adequate Humidity
Maintaining proper humidity levels is crucial for successful sprouting. Use a hygrometer to monitor the humidity in your growing space. If the humidity is too low, you can increase it by misting the air around your sprouts or placing a tray of water nearby. If the humidity is too high, use a dehumidifier or increase air circulation.
Ventilation and Air Circulation
Good air circulation is important for preventing mold or fungal growth and promoting strong, healthy plants. Use fans or open windows to ensure a steady supply of fresh air. Avoid overcrowding your plants, as this can impede airflow and increase the risk of disease.

Planting the Seeds
Determining the Right Time
Each seed variety has specific planting requirements, including the optimal time to plant. Consider the germination time and growth requirements of the seeds you’re working with. Start your seeds indoors with enough time for them to develop into healthy seedlings before transplanting them outdoors or into larger containers.
Preparing the Containers
Before planting your seeds, make sure your containers are clean and sterilized to prevent disease. Fill the containers with the seed starting mix, leaving some space at the top for watering. Gently press down the soil to provide a firm but not compacted surface for your seeds.
Sowing the Seeds
Follow the recommended planting depth for each seed variety. Using your finger or a small tool, create a shallow hole in the soil and place the seed inside. Cover the seed with soil, firming it gently. If sowing multiple seeds, provide enough spacing to allow for proper growth and avoid overcrowding.
Covering the Seeds
Some seeds benefit from being covered with a thin layer of vermiculite or a clear plastic dome to help maintain moisture levels and create a greenhouse-like environment. Follow the specific instructions for each seed variety to determine if covering is necessary.
Watering and Caring for Seedlings
Watering Schedule
Establish a consistent watering schedule for your seedlings. The frequency may vary depending on factors such as the type of seed, growing medium, and environmental conditions. Water your seedlings when the top inch of the soil feels dry to the touch, taking care not to overwater as this can lead to root rot.
Monitoring Moisture Levels
Regularly check the moisture levels of the soil to ensure it is not too dry or too wet. Stick your finger into the soil up to the first knuckle. If it feels dry, it’s time to water, but if it feels moist, hold off until the soil dries out a bit.
Providing Proper Drainage
Good drainage is essential for healthy seedling growth. Make sure your containers have drainage holes to allow excess water to escape. If using trays or saucers to catch water, empty them promptly to prevent waterlogged conditions.
Fertilizing Seedlings
Once your seedlings have true leaves, you can start fertilizing them with a diluted liquid fertilizer. Follow the fertilizer’s instructions for dilution and application rates. Avoid overfertilizing, as this can damage the delicate roots of your seedlings. Gradually increase the strength of the fertilizer as the seedlings grow.

Providing Adequate Light
Natural Light vs. Artificial Light
While some plants can thrive with only natural light, most will require additional artificial light when grown indoors. Natural light can be supplemented with artificial lighting to provide the necessary light intensity and duration for optimal growth.
Choosing the Right Light Source
LED grow lights are a popular choice for indoor sprouting due to their energy efficiency and ability to emit the specific wavelengths of light that plants need. Look for lights with a full spectrum output, which provides a balanced light spectrum similar to natural sunlight.
Positioning the Light Source
Position the grow lights about 6-12 inches above your seedlings, adjusting the height as they grow. This will ensure that the light is evenly distributed and does not cause excessive heat or light burn on the seedlings. Keep the lights on for 12-16 hours a day to mimic the length of natural daylight.
Managing Light Exposure and Duration
It’s important to monitor the amount of light exposure your seedlings receive to prevent problems such as leggy growth or light burn. If your seedlings start to appear long and spindly, they may not be receiving enough light. On the other hand, if they appear scorched or bleached, they may be getting too much light. Adjust the light duration and intensity accordingly.
Managing Temperature and Humidity
Monitoring Temperature
Maintaining the right temperature is crucial for healthy seedling growth. Most seeds require a consistent temperature range for germination and growth. Use a thermometer to monitor the temperature in your growing space and make necessary adjustments, such as using a heating mat or adjusting the room temperature.
Using Heat Mats or Thermostats
If your growing space is too cold, you can use heat mats or thermostats to provide gentle warmth to the seeds. This can help speed up germination and promote healthy root development. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe operation.
Increasing Humidity Level
If the humidity in your growing space is too low, you can increase it by misting the air around your seedlings or placing a tray of water nearby. This will create a more humid environment that helps prevent drying out of the seedlings and promotes healthy growth.
Preventing Excessive Humidity
While humidity is important, excessive moisture can lead to fungal diseases such as damping-off. Ensure proper ventilation and air circulation to prevent the buildup of excessive humidity. If necessary, use a dehumidifier or fans to promote airflow and prevent high humidity conditions.
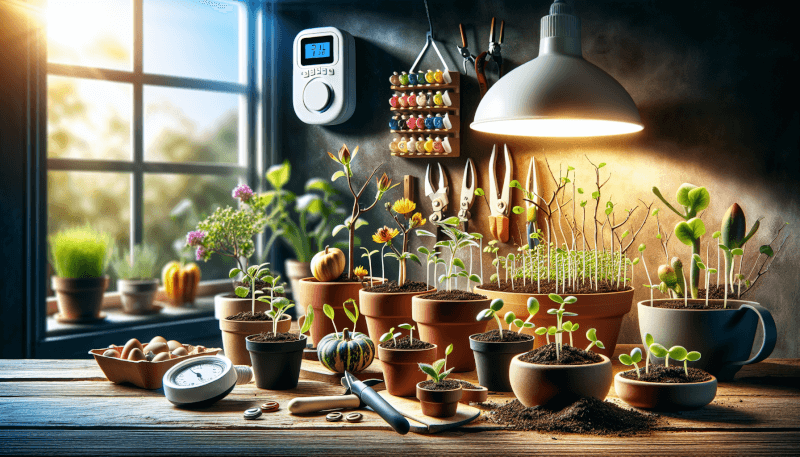
Transplanting Seedlings
Determining the Right Time for Transplanting
Transplanting is the process of moving seedlings from their starting containers to larger pots or outdoor areas. The right time for transplanting depends on the specific plant and its growth characteristics. Generally, seedlings should have a few sets of true leaves and a well-developed root system before being transplanted.
Preparing the Transplanting Area
Before transplanting, prepare the transplanting area by ensuring the soil is well-prepared and free of weeds. If transplanting into larger pots, fill them with a suitable potting mix. Gently remove the seedlings from their starting containers, being mindful of their delicate roots.
Handling the Seedlings
When handling seedlings for transplanting, it’s important to be gentle and avoid damaging the roots. Hold the seedling by its leaves or the base of the stem, taking care not to squeeze or crush the delicate plant parts. Avoid pulling on the seedling, as this can damage the roots.
Planting Seedlings in Desired Containers
Place the seedlings in their new containers or prepared outdoor areas, ensuring that the soil level matches the previous planting depth. Firmly but gently tamp down the soil around the seedling, providing support for the roots. Water the newly transplanted seedlings to help them settle into their new environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Dealing with Seedling Diseases
Seedlings are susceptible to various diseases, such as damping-off or fungal infections. To prevent these diseases, use sterile containers and soil, avoid overwatering, and ensure proper air circulation. If you notice any signs of disease, such as wilting or yellowing leaves, take immediate action by removing affected seedlings and treating the remaining ones with appropriate fungicides if necessary.
Addressing Pest Infestations
Pests such as aphids, mites, or fungus gnats can pose a threat to your indoor seedlings. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pest infestation, such as chewed leaves, sticky residue, or small flying insects. Use appropriate organic pest control methods, such as neem oil or insecticidal soap, to manage infestations and maintain healthy seedlings.
Overcoming Leggy or Spindly Seedlings
Leggy or spindly seedlings are usually a sign that they are not receiving enough light. To overcome this issue, increase the intensity and duration of light exposure. Position the grow lights closer to the seedlings or adjust their height to ensure that they receive adequate light for proper growth.
Taking Action Against Poor Germination
If you’re experiencing poor germination rates, there may be several factors at play. Ensure that you are using fresh and viable seeds, follow the proper seed treatment techniques, and maintain the correct temperature and humidity levels. If these steps do not improve germination, you may need to reassess your seed quality or growing methods.
By following these steps and taking the necessary precautions, you can successfully sprout seeds indoors and enjoy the joy of gardening year-round. Remember to enjoy the process and be patient, as growing plants from seeds requires time and attention. Happy sprouting!
